
![]()
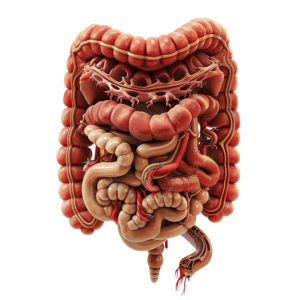
The Digestive System
The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food into nutrients, which the body uses for energy, growth, and cell repair. It consists of several organs working together to process food and eliminate waste.
![]()
Main Components of the Digestive System
1. Mouth: The starting point of digestion, where food is chewed and mixed with saliva.
2. Esophagus: A muscular tube that moves food from the mouth to the stomach
3. Stomach: Breaks down food with gastric juices.
4. Small Intestine: Absorbs nutrients into the bloodstream.
5. Large Intestine: Processes waste and absorbs water.
6. Liver & Pancreas: Produces enzymes and bile for digestion.
7. Rectum & Anus: Eliminates waste from the body.
![]()
Common Digestive Disorders
1. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): A condition where stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing heartburn.
2. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A chronic disorder affecting the large intestine, causing cramping, bloating, and diarrhea or constipation.
3. Ulcers: Open sores in the stomach lining due to excessive acid
4. Celiac Disease: An immune reaction to gluten that damages the small intestine.
5. Gallstones: Hardened deposits in the gallbladder that can cause pain and digestive issues.
6. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, leading to chronic inflammation of the digestive tract.
![]()
Prevention and Treatment
- Eat a Healthy Diet: High in fiber, fruits, and vegetables.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water daily.
- Exercise Regularly: Helps maintain a healthy digestive system.
- Avoid Smoking & Excess Alcohol: Reduces the risk of digestive disorders.
- Manage Stress: Stress can impact digestion negatively.
- Medical Treatment: Medications, probiotics, and surgery (for severe conditions).
If you experience persistent digestive problems, consult a specialist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
